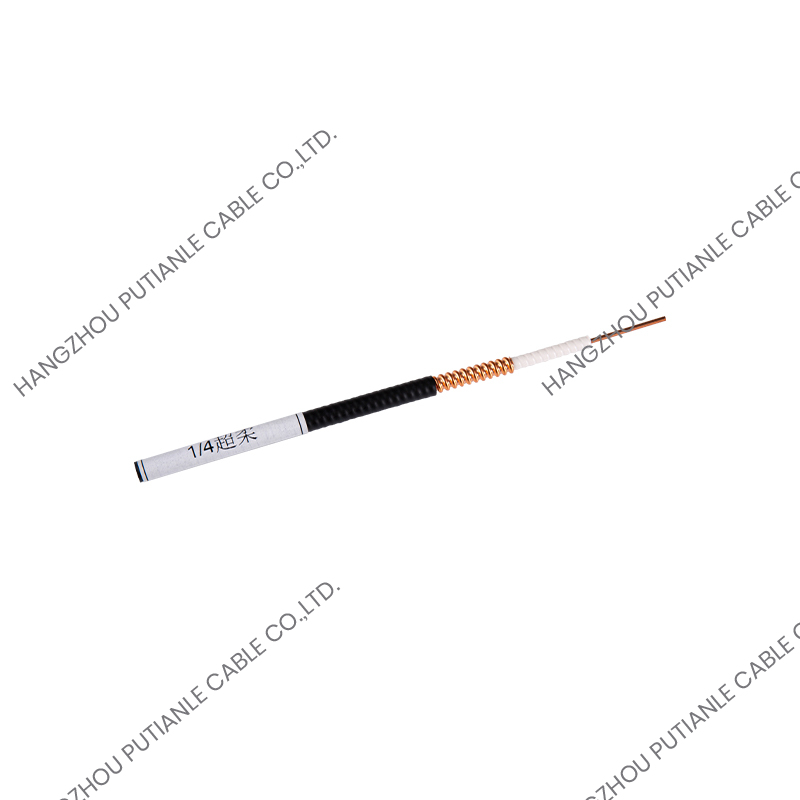
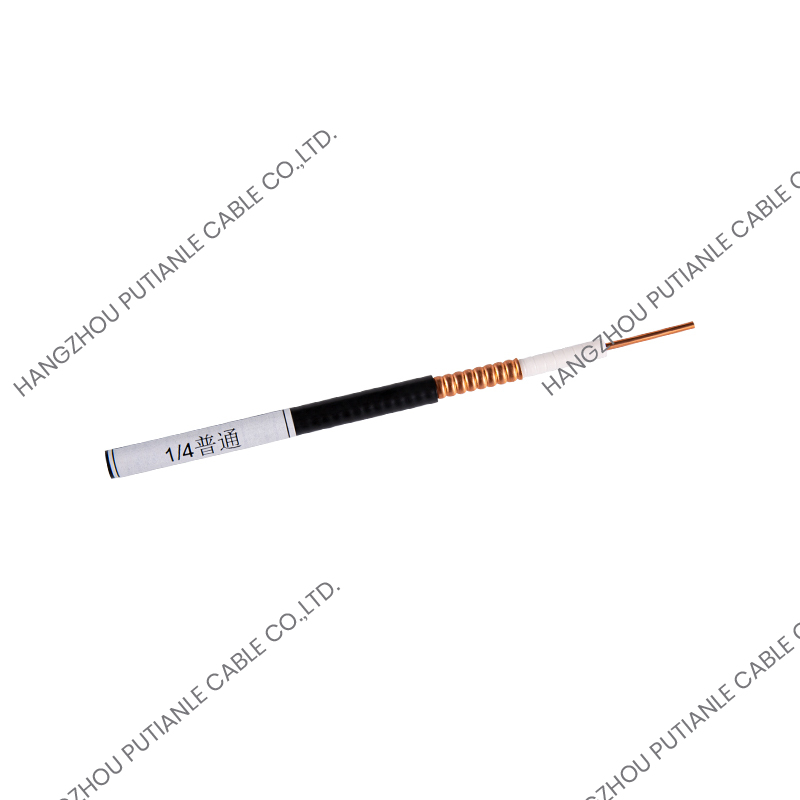
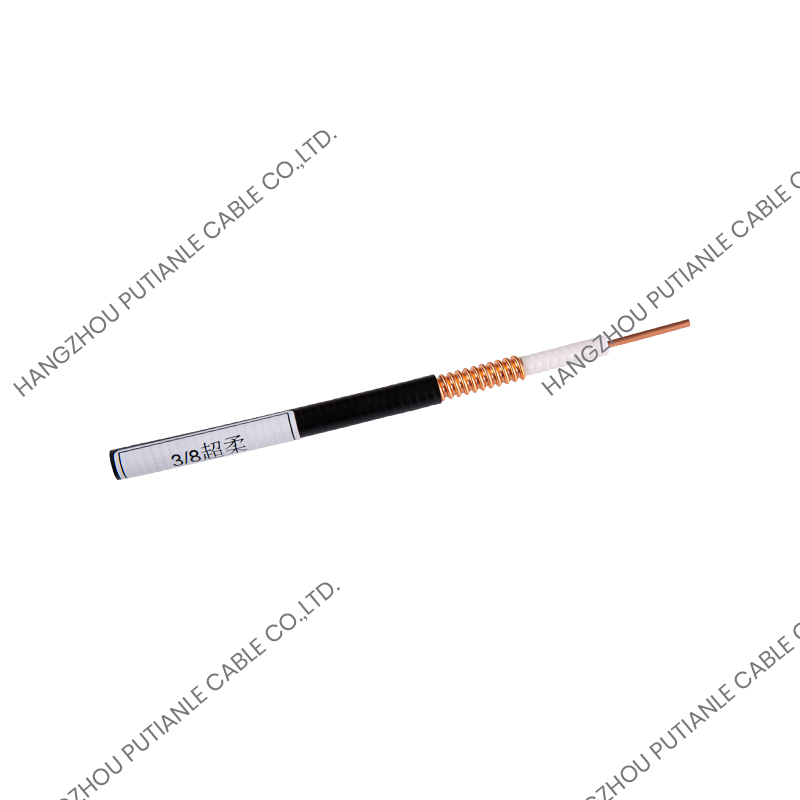
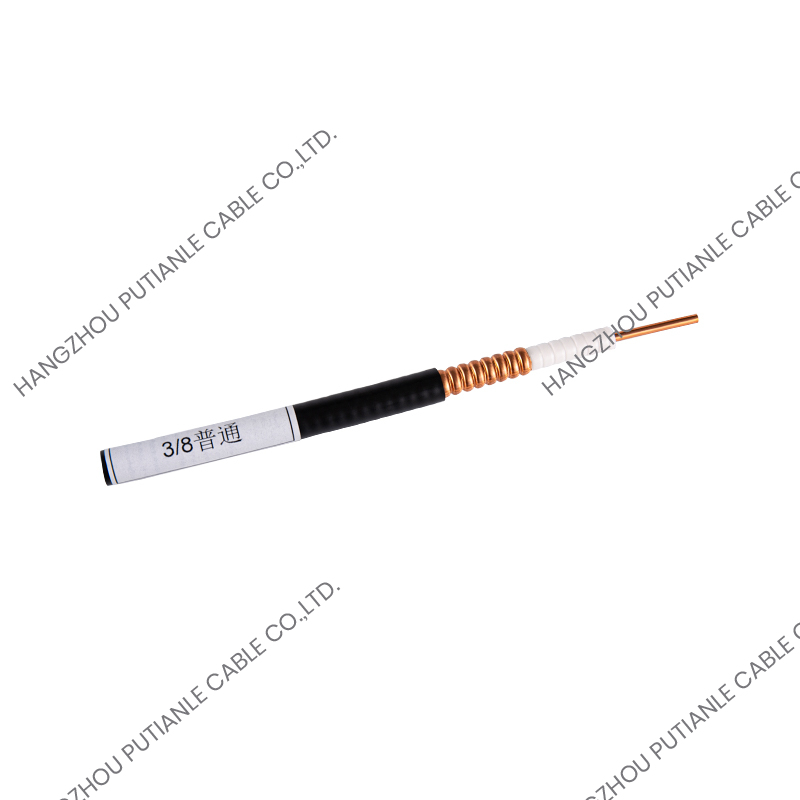
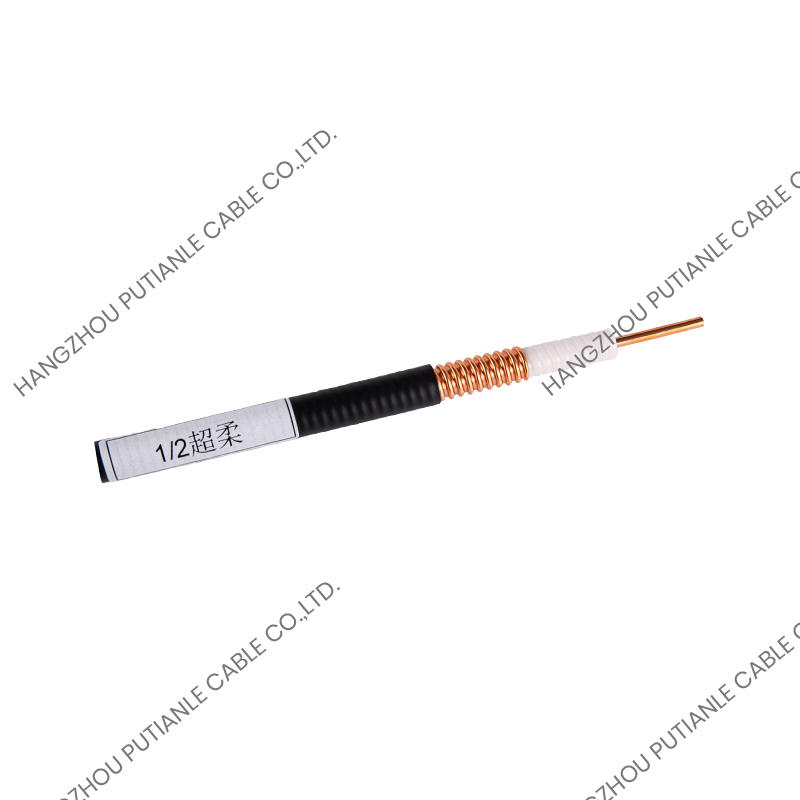
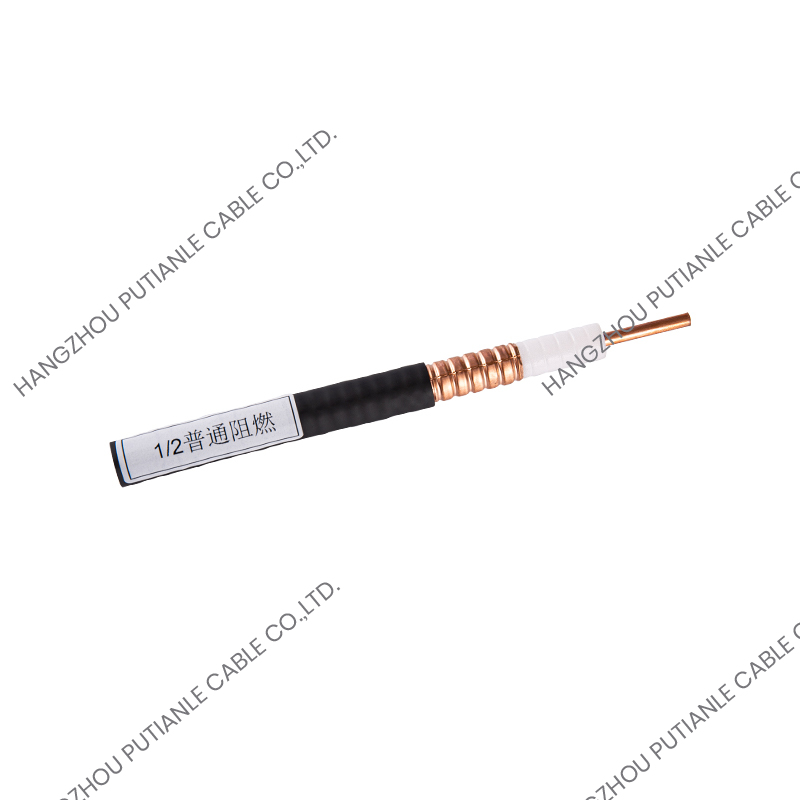
50 Ohm braiding cables are a critical component in modern communication systems, providing reliable signal transmission and impedance matching. These cables are widely used in applications ranging from RF and microwave systems to wireless networks, satellite communications, and high-frequency instrumentation. Understanding their structure, characteristics, and applications helps engineers and technicians optimize system performance.
Technical Characteristics of 50 Ohm Braiding Cables
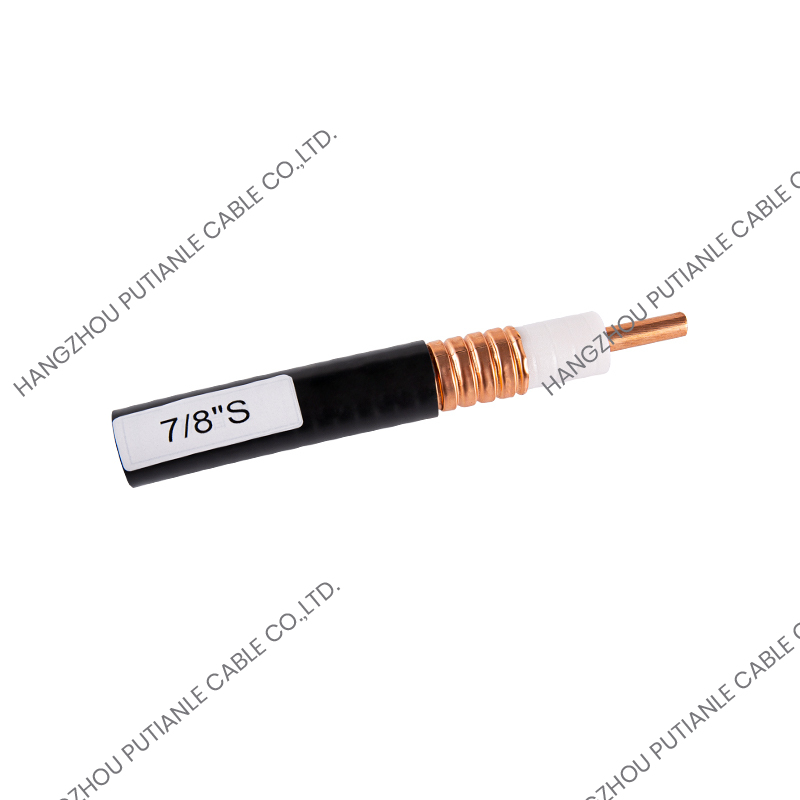
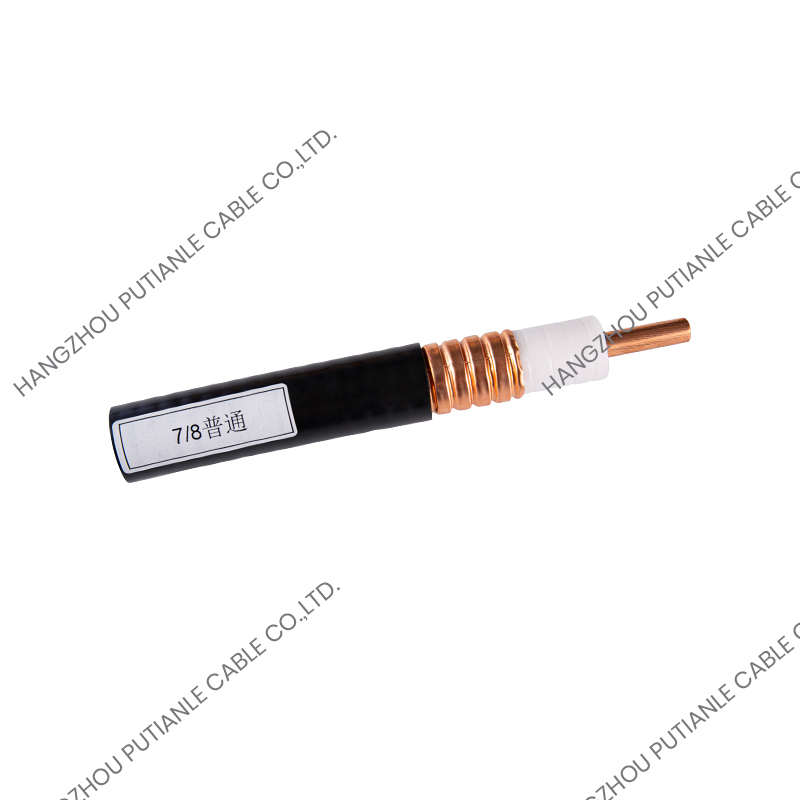
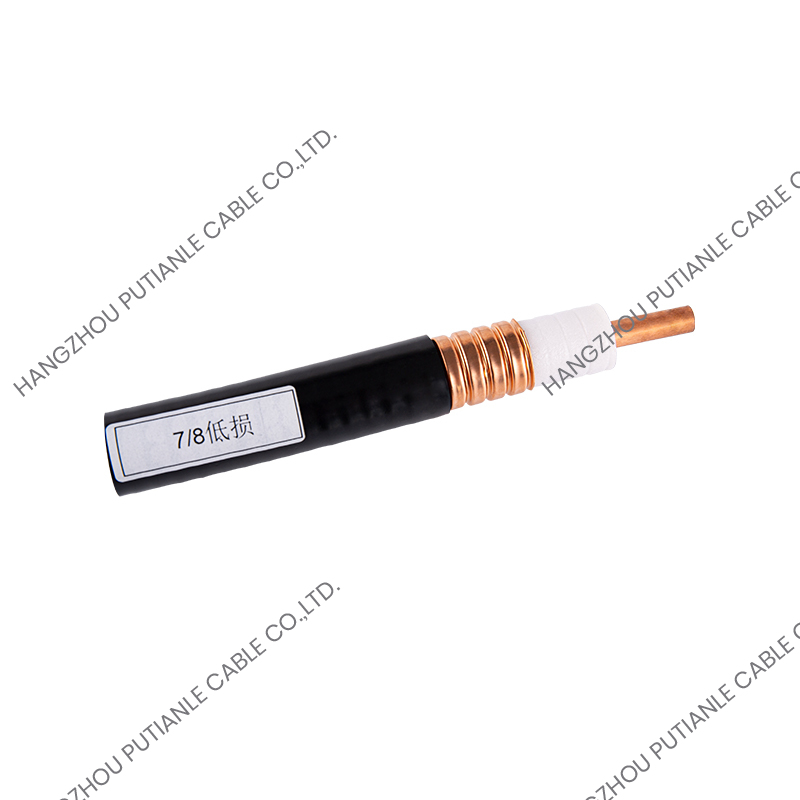
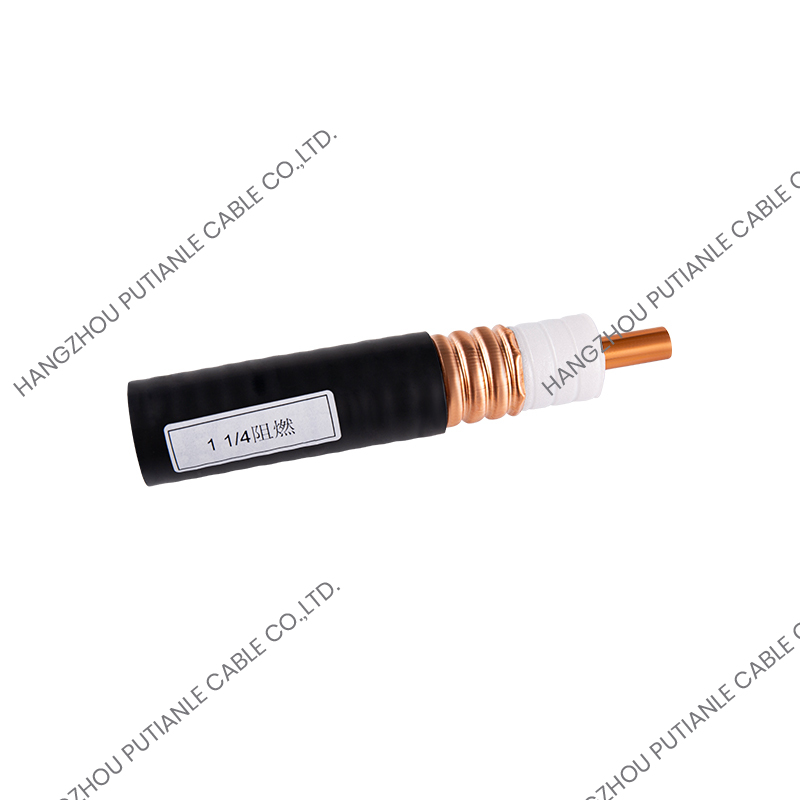
The 50 Ohm designation refers to the cable's characteristic impedance, which is the result of the relationship between the conductor and the braided shielding. This impedance ensures minimal signal reflection and maximum power transfer. These cables typically feature a solid or stranded inner conductor, a dielectric insulator, a metallic braid for shielding, and an outer protective jacket.
Conductors and Dielectric Materials
The inner conductor may be made of copper, tinned copper, or silver-plated copper to enhance conductivity. The dielectric material surrounding the conductor is designed to maintain the 50 Ohm impedance while minimizing signal loss. Common dielectrics include polyethylene (PE), foam PE, and PTFE, each offering specific advantages for flexibility, temperature tolerance, and low attenuation.
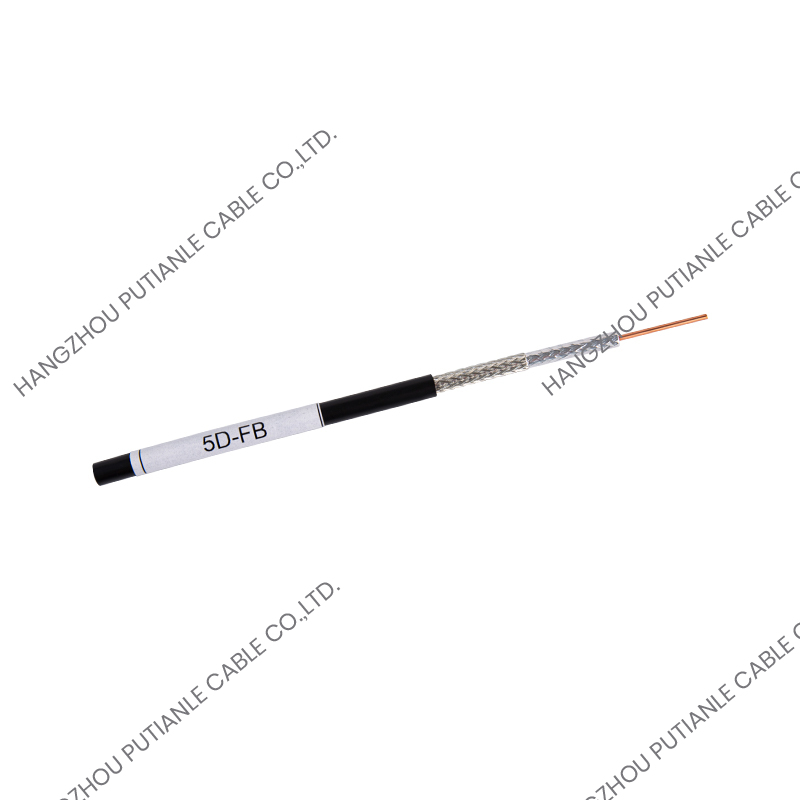
Braided Shielding
The braided shield in 50 Ohm cables provides electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection while maintaining the cable's structural integrity. The percentage of coverage and material, such as copper or tinned copper, influences the cable's effectiveness against interference. High braid coverage ensures superior shielding for sensitive RF applications.
Outer Jacket Materials
The outer jacket protects the cable from mechanical damage, UV radiation, and environmental factors. Common jacket materials include PVC, polyurethane, and PTFE, selected based on the installation environment and durability requirements.
Key Applications in Communication Systems
50 Ohm braiding cables are designed for precise impedance matching and reliable signal transmission, making them ideal for a range of communication systems. The following are key application areas:
Wireless Communication Networks
These cables are commonly used to connect antennas, base stations, and RF modules in wireless communication networks, including LTE, 5G, and Wi-Fi. Their low signal loss and consistent impedance ensure high-quality data transmission across the network.
Satellite and Aerospace Applications
In satellite and aerospace systems, 50 Ohm braiding cables transmit high-frequency signals between transceivers, antennas, and monitoring equipment. Their ability to withstand vibration, temperature extremes, and EMI makes them suitable for demanding aerospace environments.
Test and Measurement Equipment
Precision instruments in laboratories and industrial testing facilities often rely on 50 Ohm cables to maintain signal integrity. They are used in oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and network analyzers to ensure accurate measurements without distortion or reflection.
RF and Microwave Systems
In RF and microwave communication systems, maintaining consistent impedance is critical. 50 Ohm cables are preferred for transmitting signals from transmitters to antennas, waveguides, and filters. They minimize return loss and preserve signal strength over long distances.
Broadcasting and Media Networks
Broadcast systems, including television and radio, utilize 50 Ohm braiding cables to connect transmitters, receivers, and antennas. Their reliable performance ensures high-quality signal delivery with minimal interference, crucial for live broadcasting applications.
Factors to Consider When Selecting 50 Ohm Braiding Cables
Selecting the right 50 Ohm braiding cable involves several practical considerations:
- Frequency range: Ensure the cable supports the system's operating frequency with minimal attenuation.
- Shielding effectiveness: Higher braid coverage provides better EMI protection for sensitive applications.
- Flexibility: Choose cables with adequate bending radius for installation in tight spaces.
- Environmental resistance: Consider UV, temperature, and chemical resistance based on operating conditions.
- Connector compatibility: Ensure the cable terminates with connectors compatible with existing equipment.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Proper handling and maintenance of 50 Ohm braiding cables prolong their life and maintain signal integrity. Key practices include:
- Avoiding sharp bends that exceed the cable’s minimum bend radius.
- Regular inspection of connectors and shielding for corrosion or wear.
- Storing cables in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent degradation.
- Using strain reliefs to reduce mechanical stress at connection points.
- Cleaning connectors with appropriate solvents to maintain low resistance contact.
Conclusion
50 Ohm braiding cables are an indispensable component in modern communication systems, ensuring high-quality signal transmission, impedance matching, and EMI protection. From wireless networks to satellite systems, RF testing, and broadcasting, these cables play a vital role in maintaining system performance. Selecting the right cable based on frequency, shielding, flexibility, and environmental resistance, combined with proper maintenance, ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español