In today’s rapidly evolving world of electronics and electrical engineering, cable design is more than just about conducting electricity. It’s also about durability, safety, interference protection, and flexibility. One solution that has stood the test of time and continues to be widely used is the braiding cable—also known as braided cable or cable with braided shielding.
You may have seen it in your phone charger, your home entertainment system, or industrial power installations—but what exactly is a braiding cable? Why is it important, and what role does it play in various industries?
Let’s explore.
What Is a Braiding Cable?
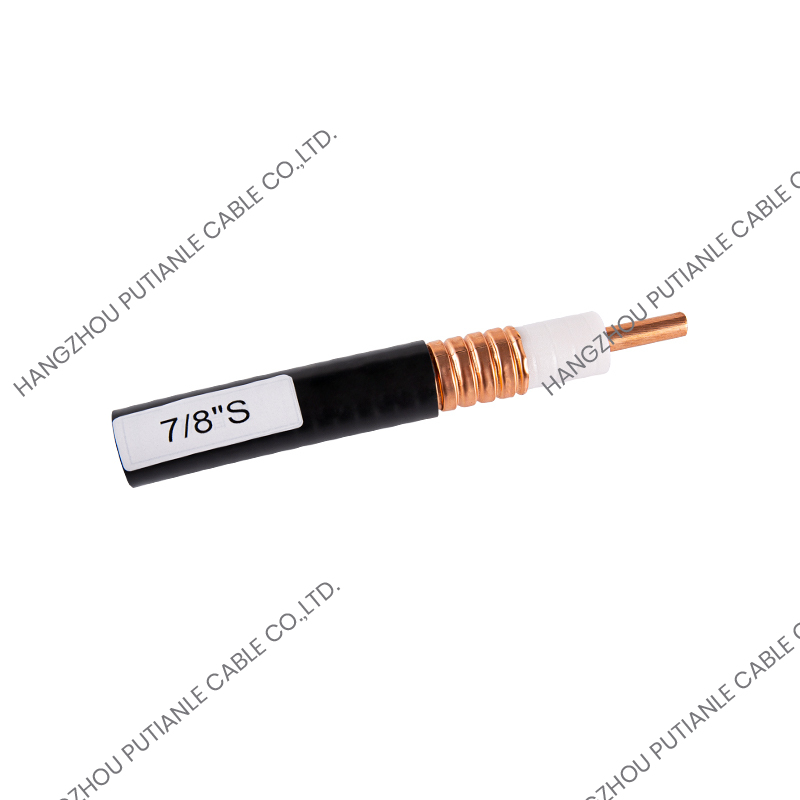
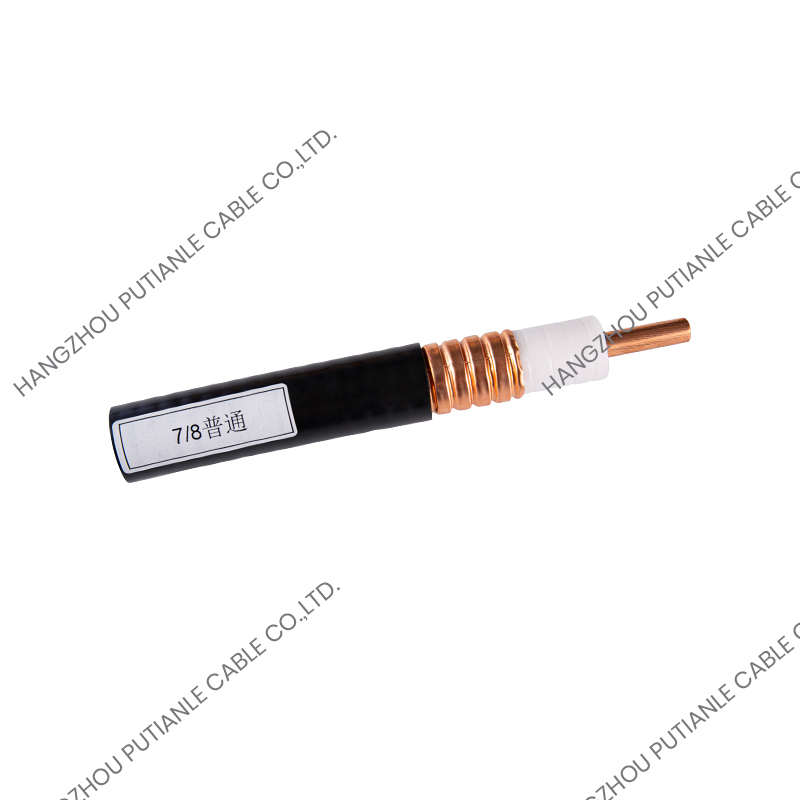
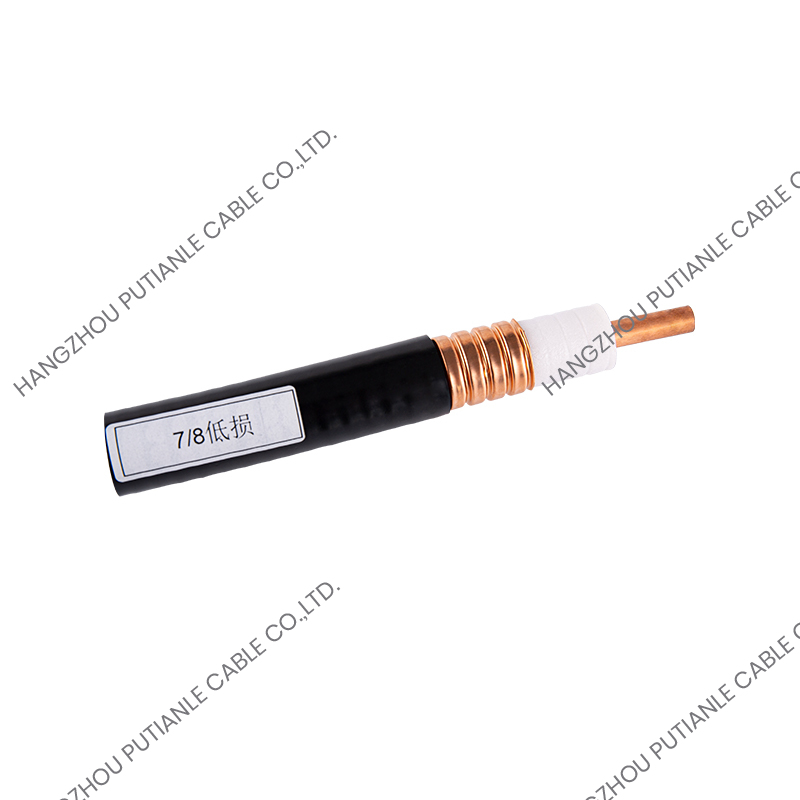
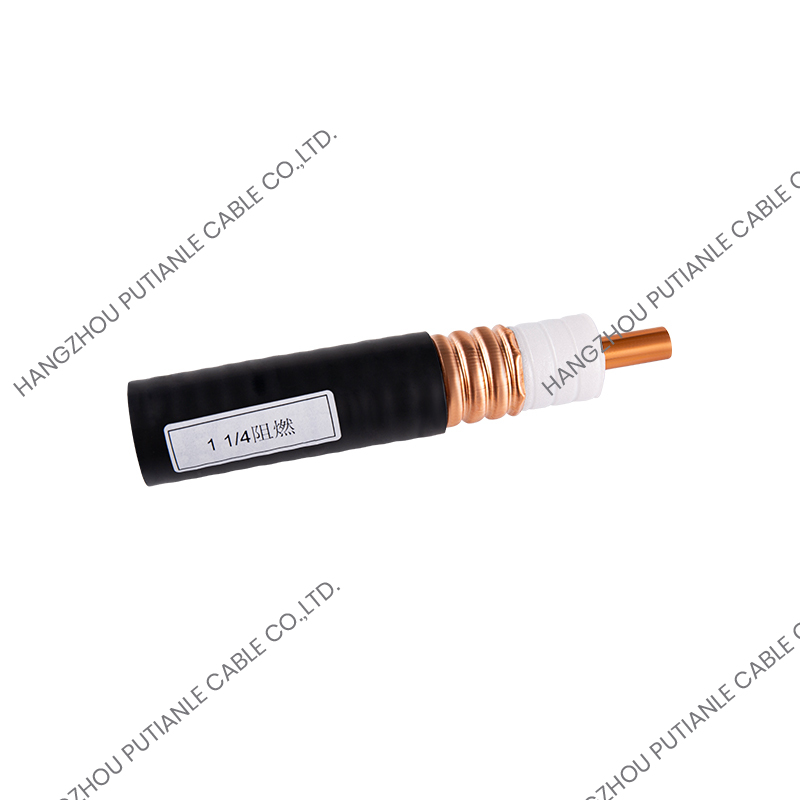
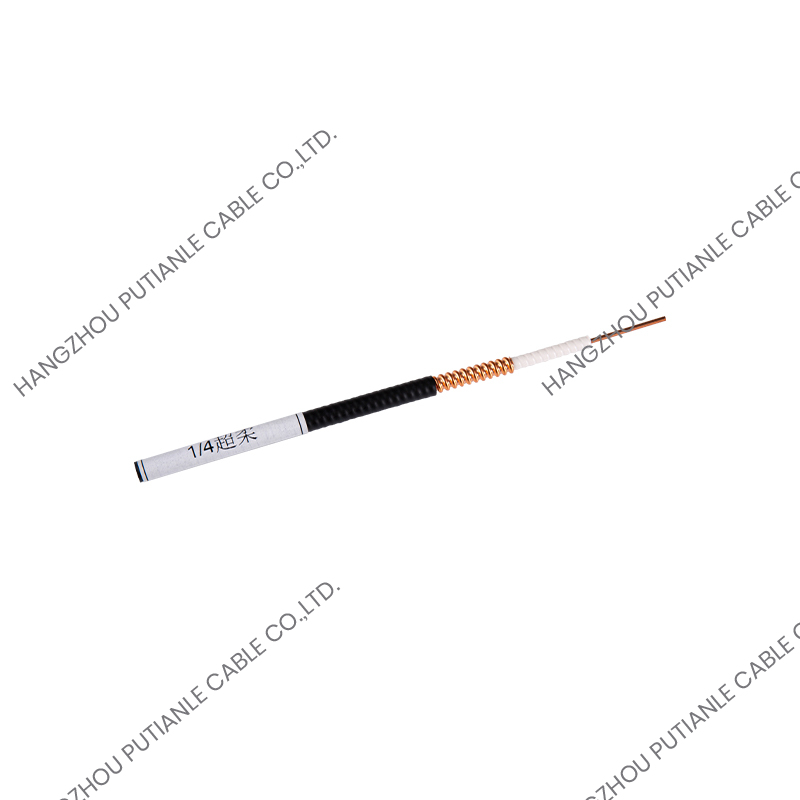
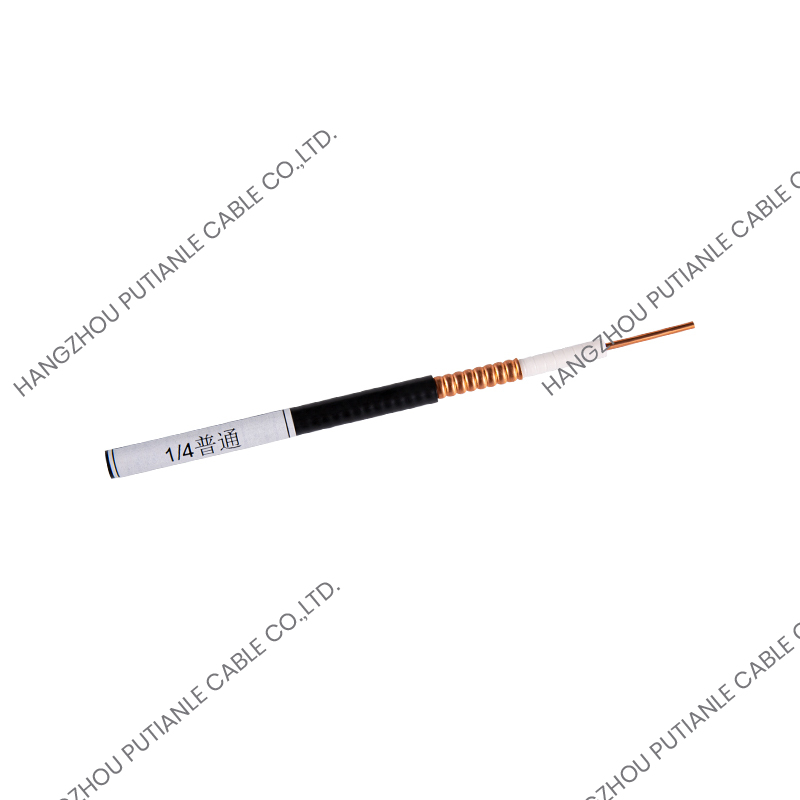
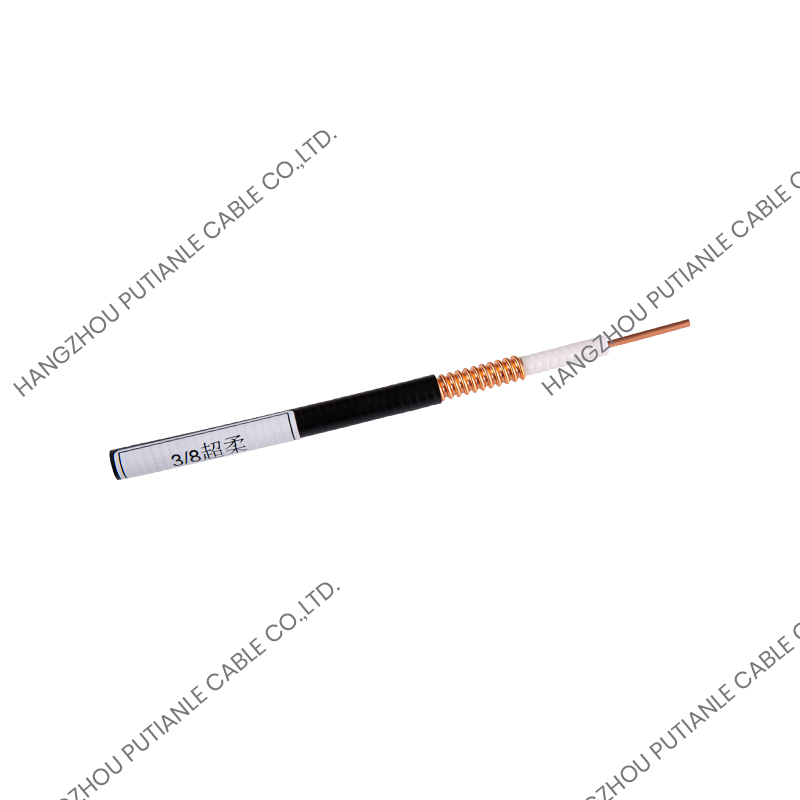
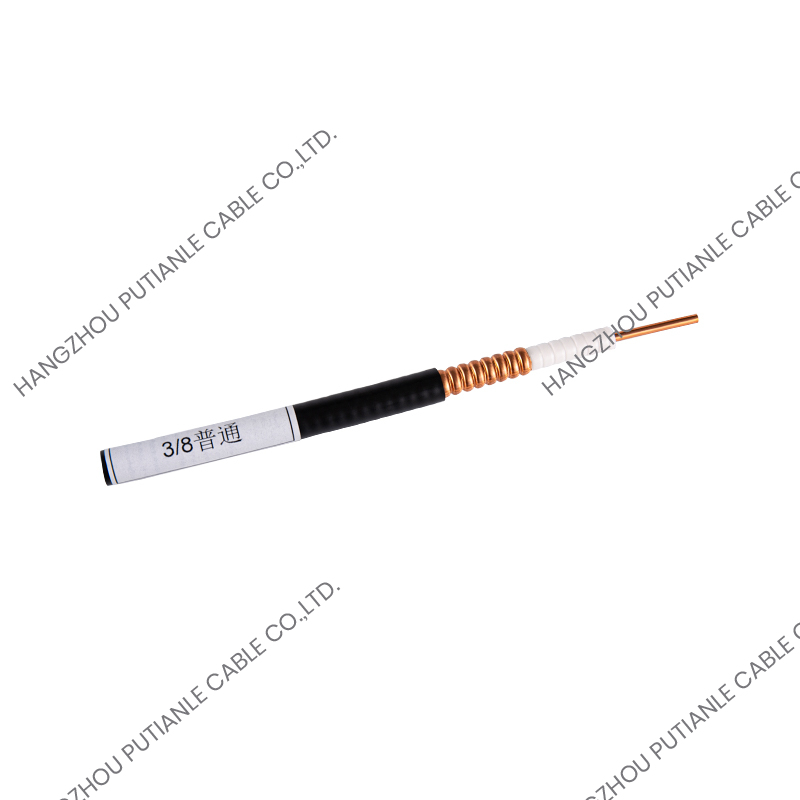
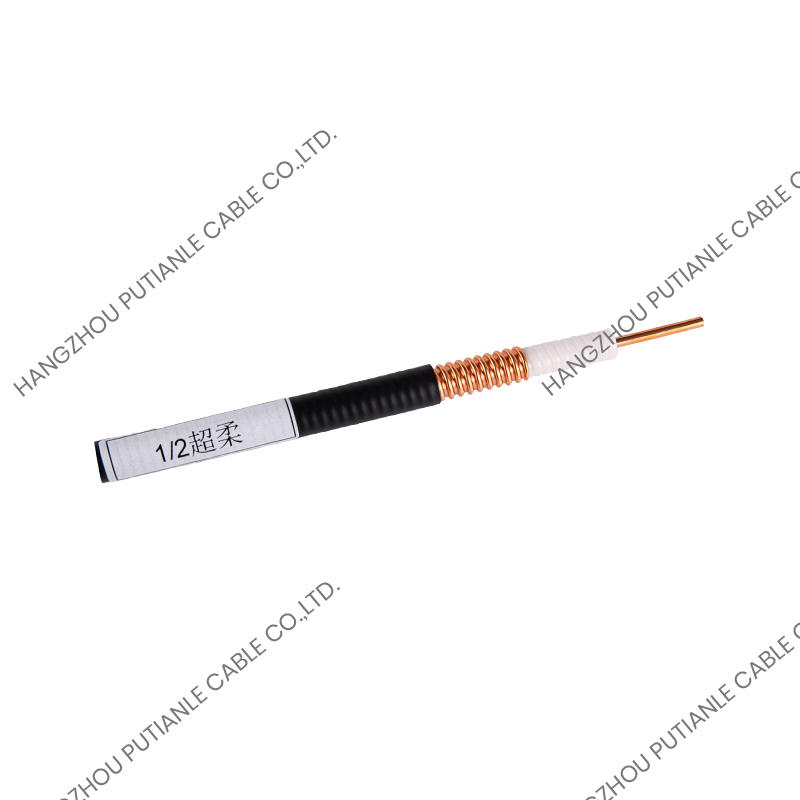
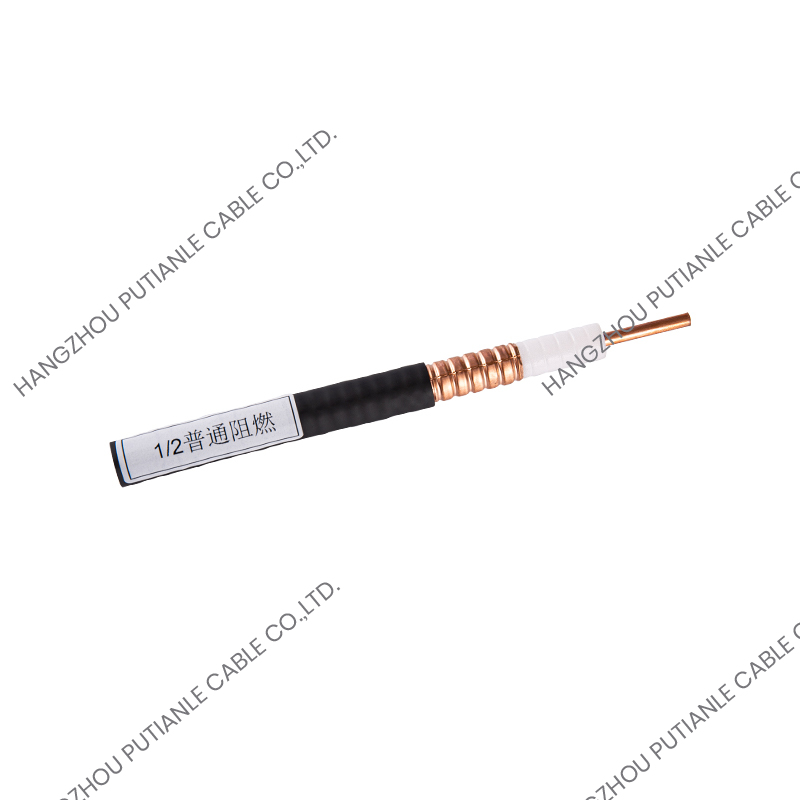
A braiding cable refers to a cable that features a woven layer of metal or synthetic fibers, known as the braid, which surrounds the inner conductors. This braided layer serves several functions, such as mechanical protection, electromagnetic shielding, and enhanced flexibility.
The braid can be made from different materials depending on its purpose:
Copper or tinned copper (for electrical shielding)
Stainless steel (for strength and corrosion resistance)
Synthetic fibers like nylon or polyester (for added flexibility or abrasion resistance)
The braiding pattern resembles a woven mesh, which allows the cable to maintain flexibility while offering strong coverage around the core.
How Does the Braiding Work?
Braiding is applied using a special machine that weaves the threads or wires around the cable’s core in an overlapping crisscross pattern. This structure ensures constant protection along the entire cable length while maintaining elasticity.
Depending on the design, the braid may cover a large portion (usually 70%–90%) of the underlying components, such as insulated wires or coaxial cable cores. The tightness and material of the braid determine its shielding effectiveness and mechanical strength.
Why Is Braiding Important?
Braided cables are valued because they solve multiple problems at once:
1. Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection
One of the most critical roles of metal braiding—especially copper—is to shield the signal inside the cable from external electromagnetic noise. EMI is common in environments with motors, radio transmitters, WiFi, or other electronics, and can corrupt data or degrade performance.
2. Mechanical Strength and Durability
The braid provides a protective layer that prevents the cable from tearing, breaking, or getting damaged under pressure, bending, or abrasion. This is particularly important in cables that are frequently moved or exposed to harsh environments.
3. Heat and Fire Resistance
Some braided cables use fireretardant materials or stainlesssteel braiding to help protect the core in hightemperature settings.
4. Enhanced Flexibility
Despite its strong structure, the braid does not compromise the cable’s ability to bend or flex. In fact, braided cables often outlast nonbraided ones in repeated motion applications like robotics, charging cables, or musical instruments.
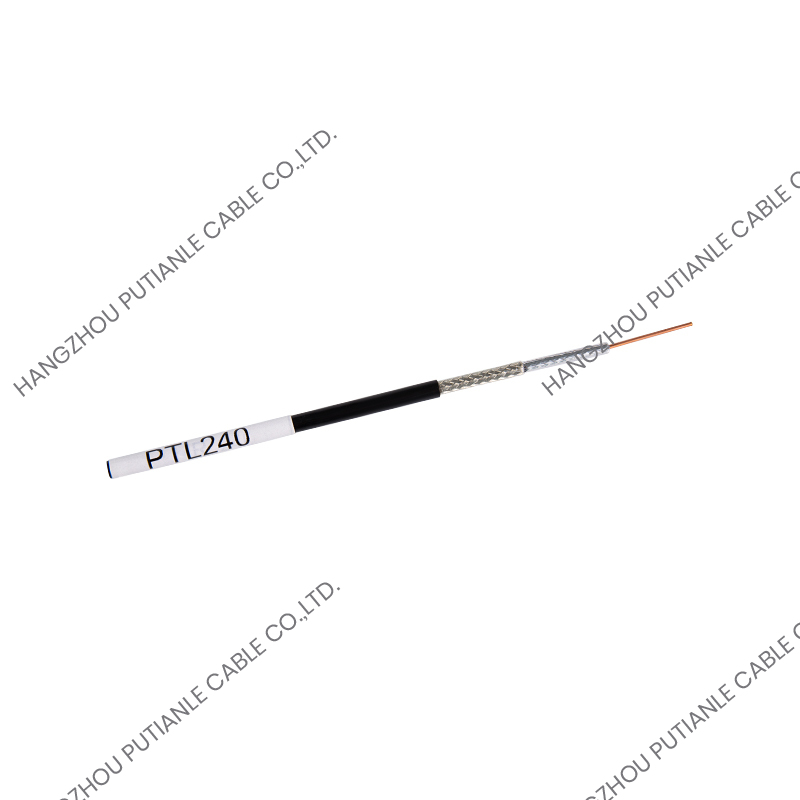

Where Are Braiding Cables Used?
Braided cables are versatile and found in a wide variety of environments:
Consumer Electronics: USB charging cables, HDMI cables, and gaming peripherals often use nylonbraided exteriors for enhanced durability and style.
Automotive Wiring: Braided cables are used in car engines and dashboards to prevent interference with electrical systems and ensure longlasting performance.
Aerospace and Military Applications: Due to extreme conditions, cables in aircraft and defense equipment often use metal braided shielding for reliability and EMI protection.
Industrial Automation: Machinery and robotics often use braided cables that can withstand motion, vibrations, and electrical noise.
Audio and Musical Equipment: Braided shielding in audio cables minimizes static and ensures clear sound signals.
Data and Communication Systems: Coaxial cables often use braided copper shields to protect data transmission.
Advantages of Braided Cables
Braiding cables offer several key advantages that make them the preferred choice in both professional and everyday settings:
Longer lifespan due to physical protection
Reduced signal loss or corruption from outside interference
Cleaner and more reliable connections
Better resistance to cuts, pinching, and environmental stress
Stylish appearance in consumer devices, especially with fabric or color braiding
Are There Any Limitations?
While braided cables are durable and effective, they do have a few limitations:
Cost: More expensive than unshielded or foilshielded cables due to materials and manufacturing.
Weight: Metalbraided cables are heavier, which may be a factor in certain lightweight designs.
Flexibility limits: Some tight braids may reduce flexibility compared to loose or spiral shielding.
Still, in most use cases, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks—especially when signal integrity and cable strength are priorities.
Conclusion
A braiding cable is much more than just a wire wrapped in fancy mesh. It’s a carefully engineered solution to realworld electrical, mechanical, and signalrelated problems. From homes and offices to factories and airplanes, braided cables ensure that the electricity and data we rely on flow safely and efficiently.
Whether you need durability, interference protection, or both, braided cables provide a smart and reliable answer—proving that in electrical engineering, what’s on the outside is just as important as what’s on the inside.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español