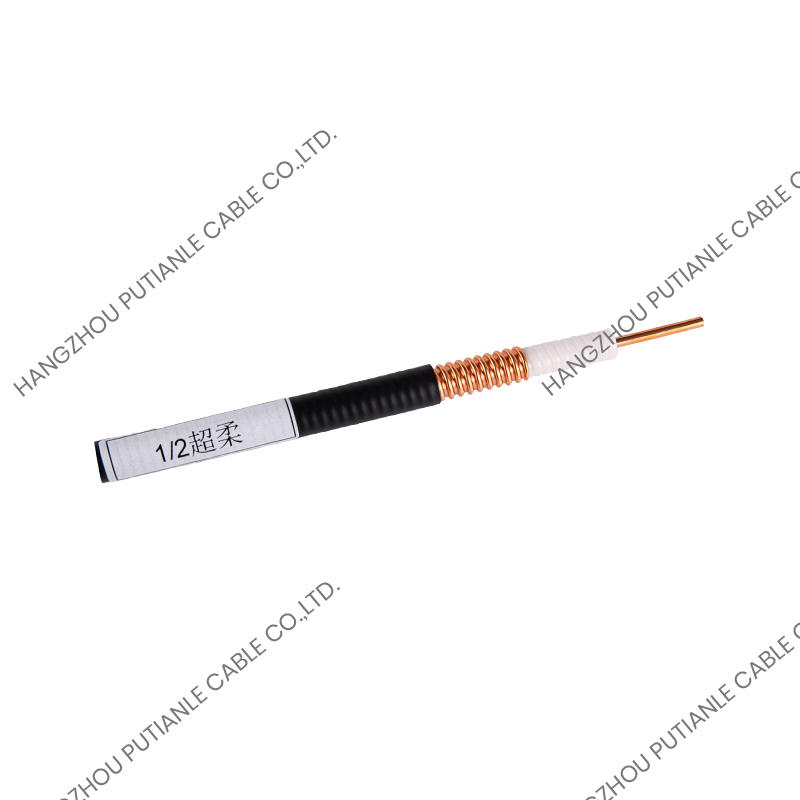
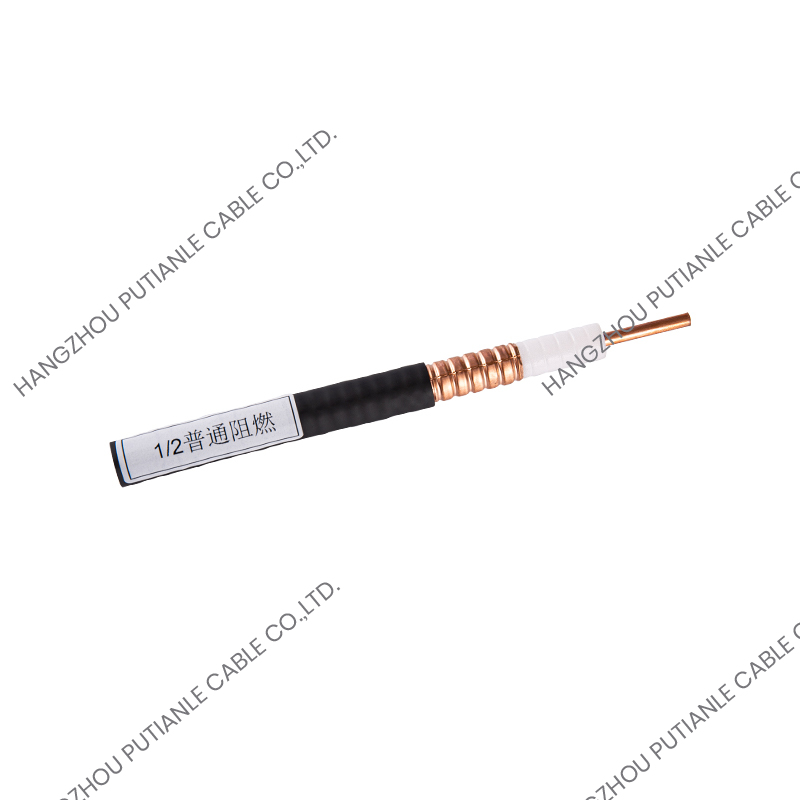
In many engineering projects such as wireless communication, RF transmission, experimental equipment, and high-frequency measurement, 50 ohm braided cable is an indispensable signal transmission carrier. Although there are many types of 50 ohm coaxial cables on the market, improper selection may lead to large signal loss, system instability, and even equipment damage. Therefore, understanding how to choose the right 50 ohm braided cable is crucial to ensuring project performance.
1. Why choose 50 ohms?
50 ohm impedance is the most common standard in radio frequency (RF) systems, mainly because it strikes the best balance between power carrying capacity and signal loss. 50 ohm systems are widely used in wireless transmission, antenna systems, Wi-Fi, LTE, radar, and laboratory test instruments.
2. What is 50 ohm braided cable?
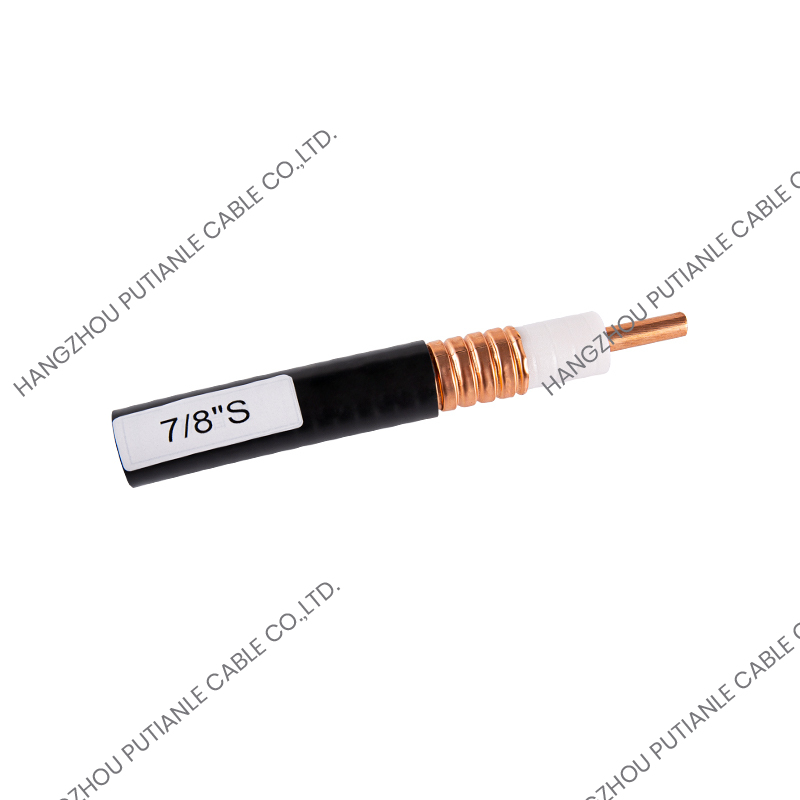
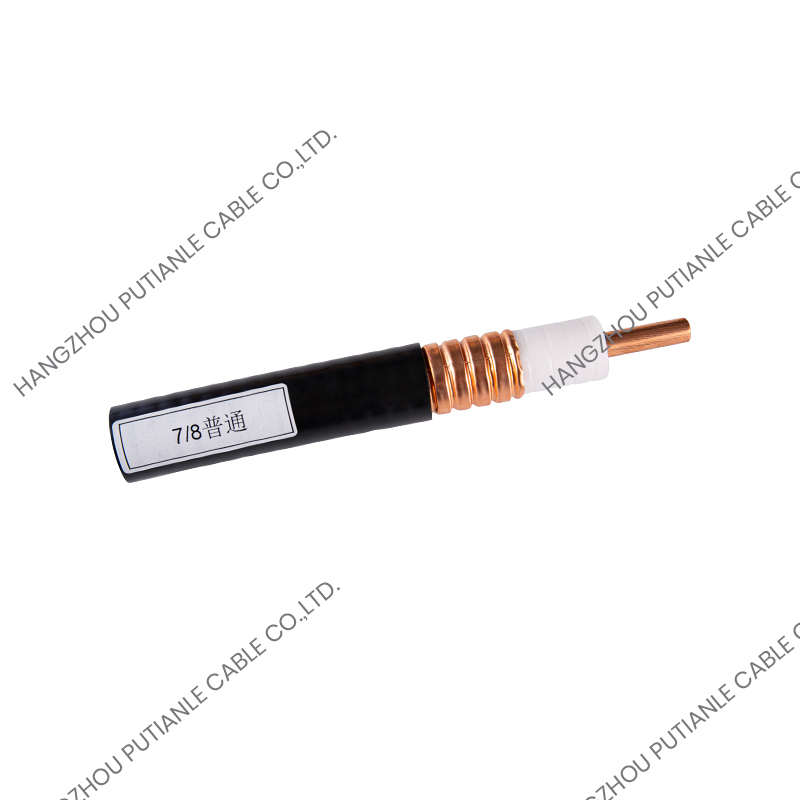
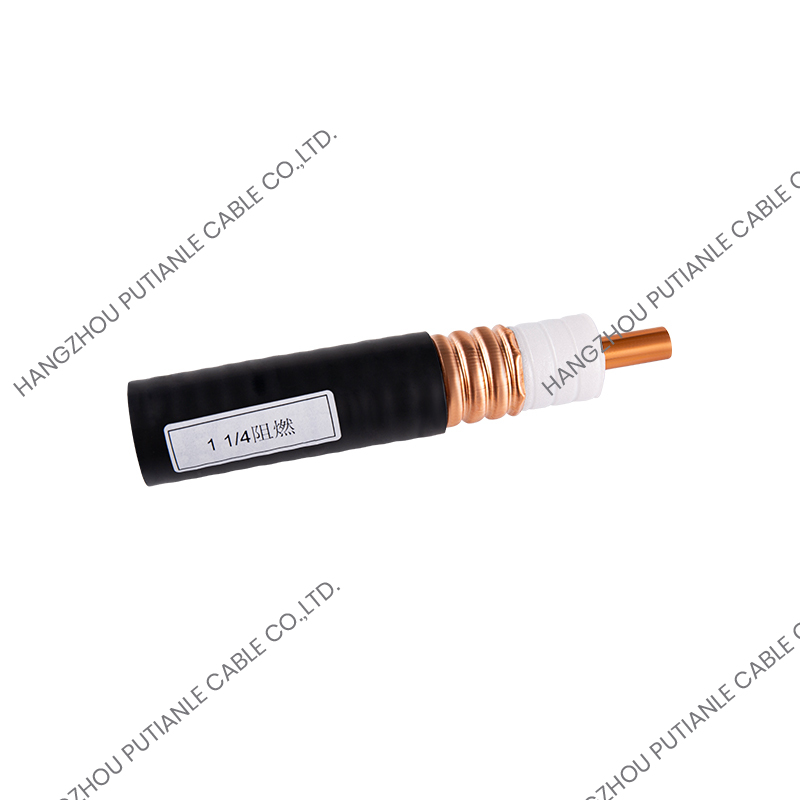
50 ohm braided cable is a coaxial structure cable consisting of an inner conductor, an insulation layer, a metal braided shielding layer (or multi-layer shielding), and an outer sheath. The function of its metal braiding layer is to resist electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure the stable transmission of high-frequency signals.
3. Key parameters to pay attention to when purchasing
1. Impedance
Always make sure the impedance of the cable is 50 ohms to match the interface impedance of the device. Impedance mismatch will lead to signal reflection (increased SWR) and reduced transmission efficiency.
2. Frequency Range
Different models of 50 ohm cables have different upper frequency limits, for example:
RG-58: supports up to 1GHz, suitable for ordinary RF equipment;
RG-142, LMR-400: higher frequency range, suitable for 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless communication;
For high-frequency microwave projects, it is recommended to use low-loss cables (such as LMR series) with lower loss.
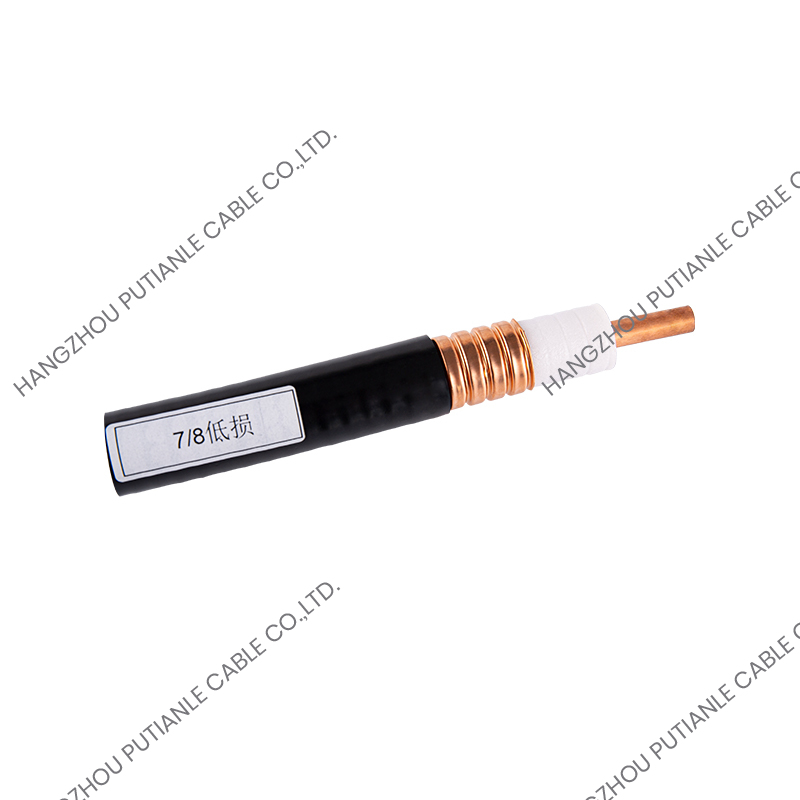
3. Attenuation
The longer the cable length, the greater the signal loss. Check the "Attenuation Value (dB/100m)" in the product data sheet, and choose a model with low loss to effectively reduce signal attenuation.
4. Flexibility and outer diameter
If the project requires frequent bending and installation in a narrow space, it is recommended to choose a model with higher flexibility and smaller outer diameter;
If it is used in fixed occasions, you can choose a model with stronger rigidity and better structural stability.
5. Shielding performance
Cables with high braiding density and double or triple shielding (braiding + foil) have stronger anti-interference ability and are suitable for industrial or experimental environments with severe EMI.
6. Connector compatibility
Make sure that the selected cable can match the connector type required by the project (such as SMA, BNC, N-type, TNC, etc.), and ensure that the connector impedance is the same as 50 ohms.
4. Purchase suggestions and precautions
Make an estimate before the project starts: calculate the required cable length and reserve 1~2 meters of redundancy for routing;
Check the technical specification sheet: manufacturers usually provide detailed electrical performance indicators, and should focus on frequency range and attenuation values;
Choose well-known brands or qualified certified products: such as Times Microwave, Belden, Amphenol, etc. to ensure product quality and consistency;
Use professional connector and connector assembly tools: avoid impedance mismatch caused by poor manual production.
Choosing the right 50 ohm braided cable does not mean "one cable for all applications". The correct selection can significantly improve project stability, transmission efficiency and system life. Considering the project environment, frequency requirements, anti-interference requirements and other factors, scientific material selection from a professional perspective can truly protect your engineering project.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español