Cables are the lifelines of modern electrical and electronic systems, transmitting power, signals, and data reliably across various applications. Among the many types of cables, braiding cables stand out for their strength, flexibility, and electromagnetic shielding capabilities. But what exactly is a braiding cable, how is it made, and why is it so widely used? This article explores its construction, working principle, advantages, applications, and maintenance considerations.
1. What Is a Braiding Cable?
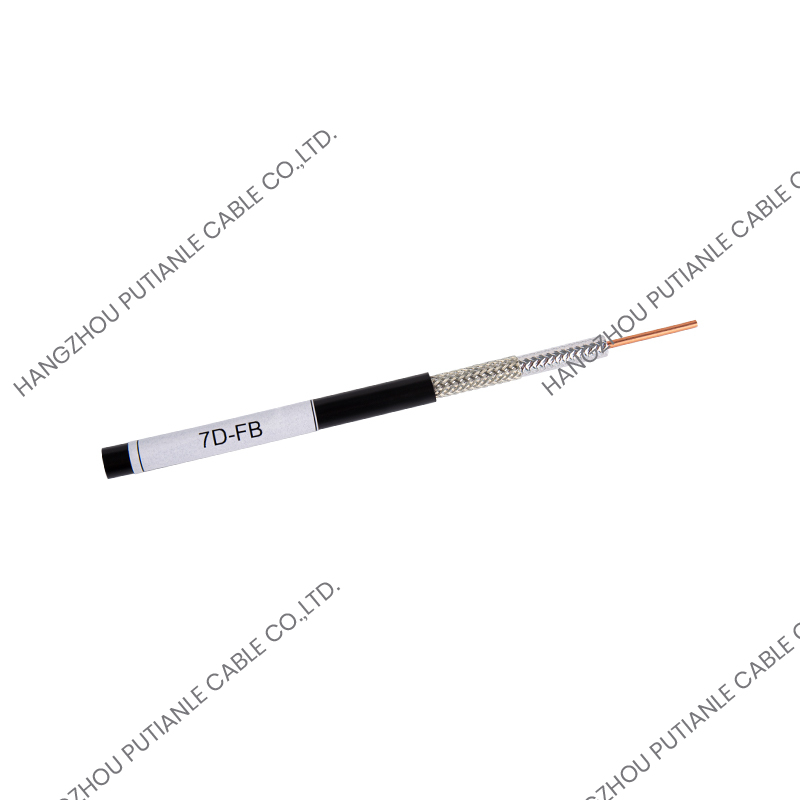
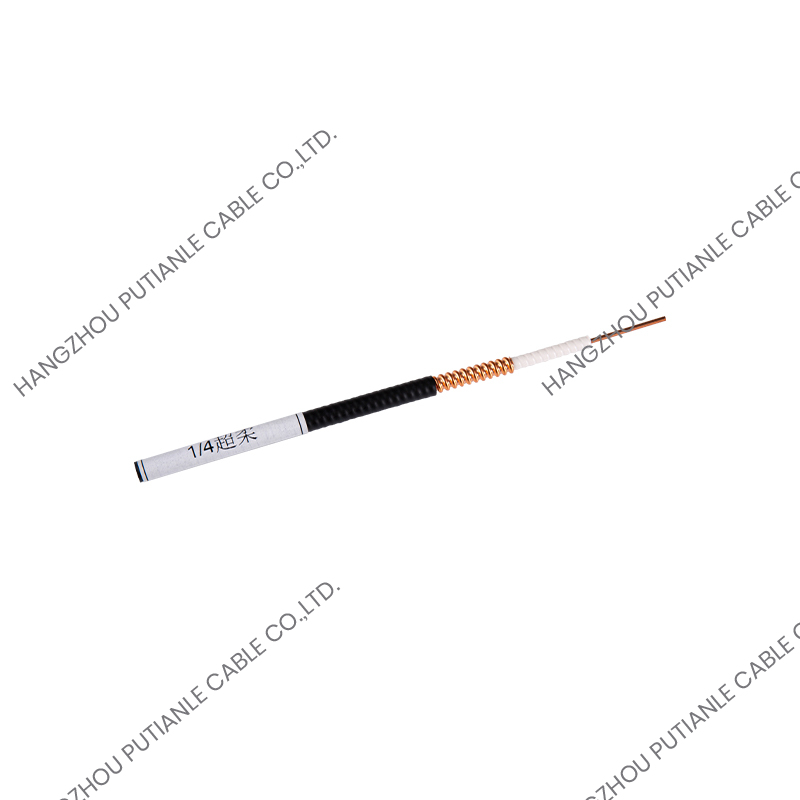
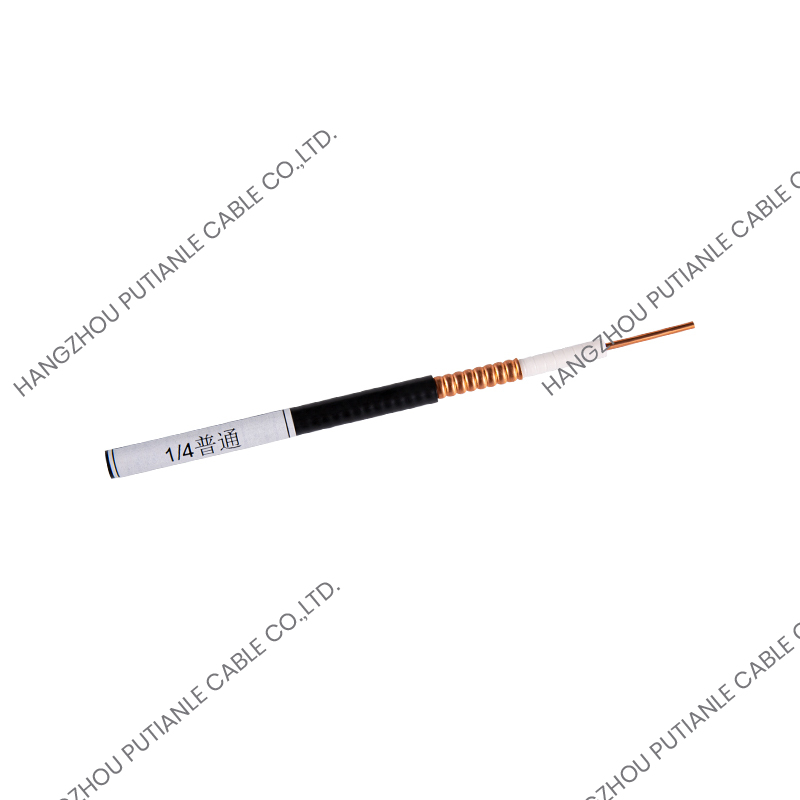
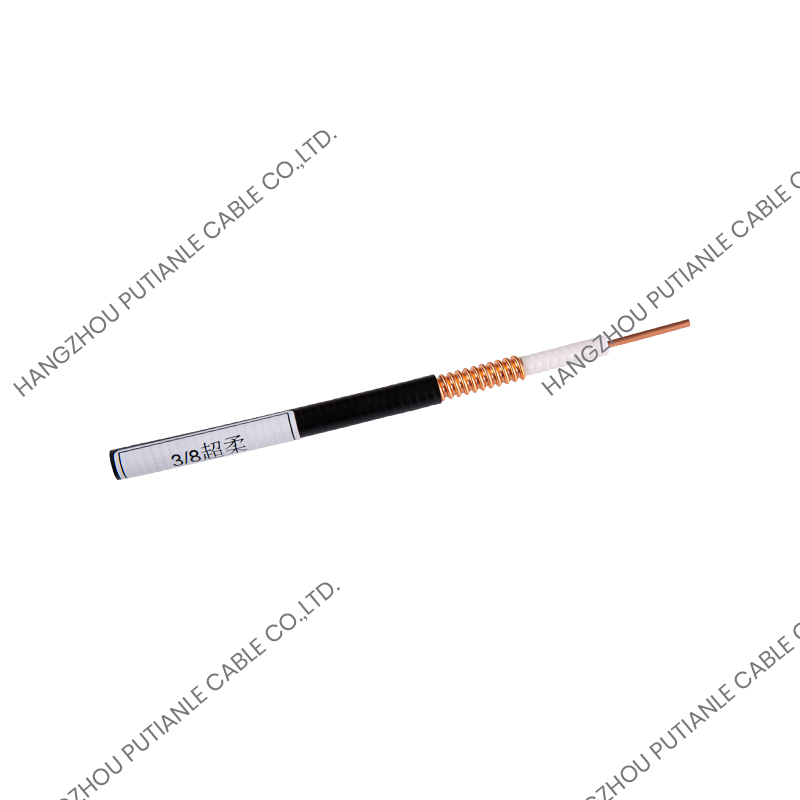
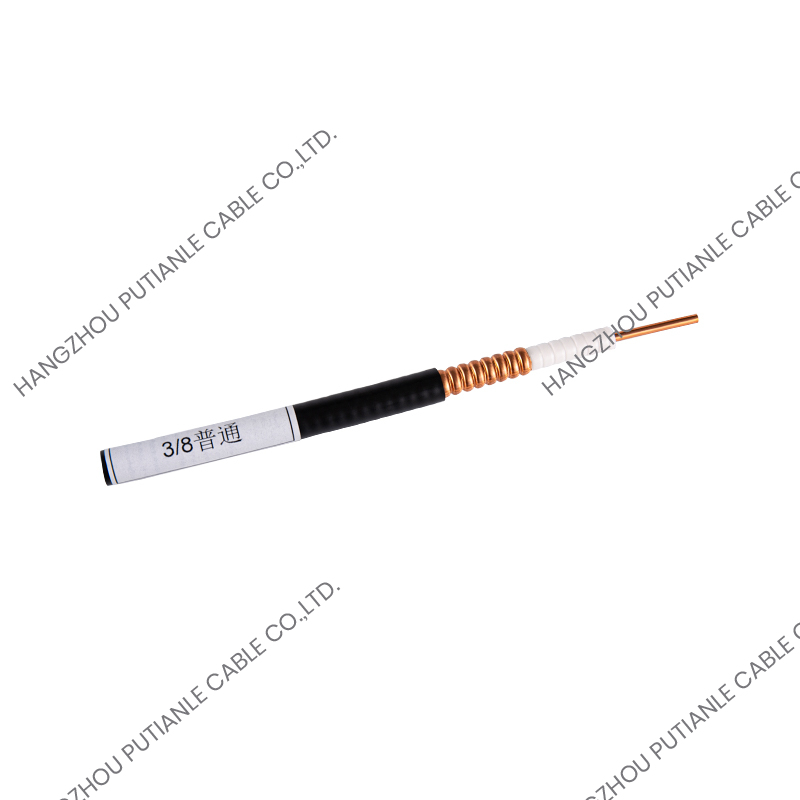
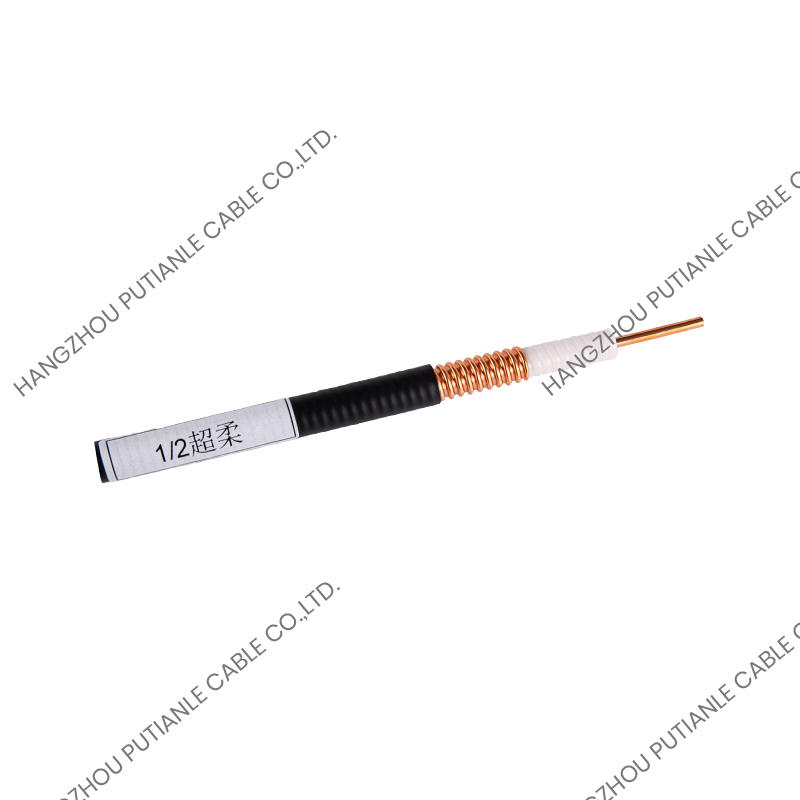
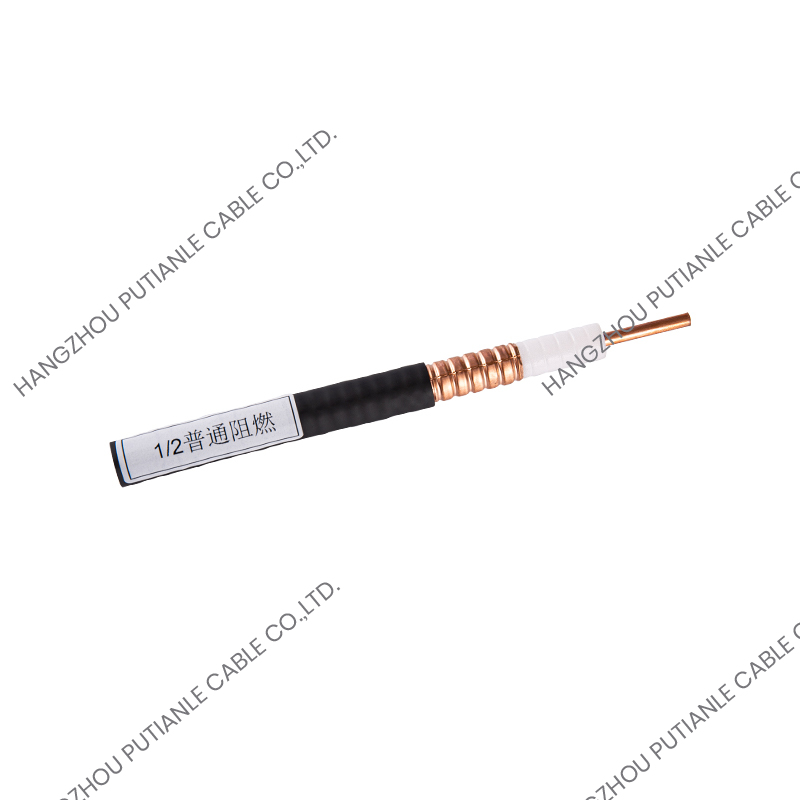
A braiding cable is a type of cable in which a conductive or protective layer of wire is woven into a braid around the core conductor or insulated wire. This braided layer may consist of copper, aluminum, stainless steel, or synthetic fibers, depending on the cable’s intended function.
The braided layer can serve multiple purposes:
- Electromagnetic shielding – Protects signals from interference.
- Mechanical reinforcement – Increases tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
- Flexibility – Allows the cable to bend and twist without breaking.
Braided cables are commonly used in power transmission, electronics, automotive wiring, and industrial applications where durability and signal integrity are essential.
2. How Does a Braiding Cable Work?
The performance of a braiding cable comes from its unique woven structure:
- Core Conductor – The main copper or aluminum wire carries the electrical current or signal.
- Insulation Layer – A polymer layer surrounds the conductor, preventing short circuits and electrical leakage.
- Braided Shield – Fine wires are woven around the insulated conductor in a crisscross pattern, providing mechanical protection and electromagnetic shielding.
- Outer Jacket (Optional) – For additional protection against environmental factors, such as moisture, heat, or abrasion.
This braided structure ensures high flexibility, even under continuous bending, while the shielding prevents signal interference from nearby electromagnetic sources.
3. Key Features and Advantages
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
| EMI/RFI Shielding | Braided copper or aluminum layer blocks electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference | Protects signal integrity in sensitive electronics |
| High Flexibility | Braided structure allows bending and twisting | Ideal for robotic, automotive, and dynamic applications |
| Mechanical Strength | Reinforces the core cable against pulling, crushing, and abrasion | Extends cable lifespan in harsh environments |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion and environmental damage | Reduces maintenance and replacement costs |
| Customizable Coverage | Braiding coverage can range from 50% to 95% | Balances shielding efficiency and flexibility |
| Thermal Stability | Can handle moderate heat without deformation | Suitable for industrial and automotive applications |
| Lightweight | Provides strength without significantly increasing weight | Convenient for portable and mobile equipment |
4. Applications of Braiding Cables
- Automotive Industry – Provides durable wiring for engines, sensors, and electronic control units.
- Electronics – Shields signal and data cables in computers, audio equipment, and communication devices.
- Industrial Machinery – Protects control and power cables in high-vibration and abrasive environments.
- Aerospace and Defense – Offers lightweight, strong, and EMI-shielded cables for aircraft and defense systems.
- Telecommunications – Ensures signal integrity in data transmission networks.
- Robotics – Flexible braided cables withstand repetitive bending and motion in robotic arms and automated machinery.
5. How to Select the Right Braiding Cable
-
Conductor Material
- Copper for high conductivity, aluminum for lightweight applications.
-
Braiding Material
- Copper for maximum shielding, stainless steel for strength, synthetic fibers for lightweight reinforcement.
-
Braid Coverage
- High coverage (90–95%) for sensitive signal cables; lower coverage (50–70%) for flexible power cables.
-
Cable Diameter and Core Size
- Match to the required current, voltage, and mechanical load.
-
Environmental Resistance
- Select outer jackets and braiding materials resistant to moisture, chemicals, or UV exposure if necessary.
-
Flexibility Requirements
- High-motion applications need tighter braiding with smaller strand diameters for better flexibility.
6. Maintenance Tips for Braiding Cables
- Regular Inspection – Check for frayed braids, exposed conductors, or damaged insulation.
- Avoid Excessive Bending – Respect minimum bend radius to prevent internal wire damage.
- Keep Clean – Remove dirt, dust, and corrosion that may affect electrical contact or shielding.
- Secure Connections – Ensure braids are properly terminated to maintain EMI shielding effectiveness.
- Replace Damaged Cables – Frayed or broken braids reduce mechanical strength and shielding efficiency.
7. Benefits of Using Braiding Cables
- Signal Integrity – Braided shielding prevents electromagnetic interference from disrupting signals.
- Durability – Resistant to mechanical stress, abrasion, and environmental factors.
- Flexibility – Allows repeated bending, twisting, and movement without damage.
- Versatility – Suitable for power, control, and data transmission in diverse industries.
- Cost Savings – Reduced maintenance, longer lifespan, and minimized downtime.
8. Conclusion
Braiding cables are essential for modern electrical and electronic systems where mechanical strength, flexibility, and signal integrity are critical. The braided structure not only provides excellent electromagnetic shielding but also reinforces the cable against mechanical stress.
By carefully selecting the conductor, braiding material, coverage, and environmental protection, engineers can design cables that meet demanding industrial, automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications requirements. Proper maintenance ensures long-term performance, reliability, and reduced operational costs.
For industries requiring durable, flexible, and interference-resistant wiring, investing in high-quality braiding cables is a smart decision that ensures efficiency, safety, and reliability across all applications.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español